Facts About : Zimbabwe
Facts About Zimbabwe - Your entry point into Zimbabwe
History
Zimbabwe, formerly known as Southern Rhodesia, has a complex history that includes early Bantu migrations, the rise of the Great Zimbabwe civilization in the 11th century, British colonization in the 19th century, and independence in 1980 following a protracted liberation struggle. Robert Mugabe became the first Prime Minister, and later President, leading the country for nearly four decades.
Geography
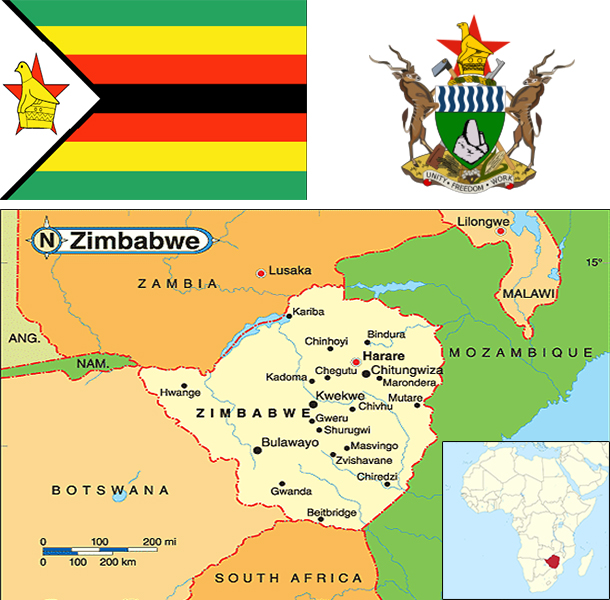
Located in southern Africa, Zimbabwe is landlocked and bordered by South Africa, Botswana, Zambia, and Mozambique. Major rivers include the Zambezi and Limpopo. Its terrain consists mostly of high plateau with higher central hills and mountains in the east. The climate is tropical but moderated by altitude.
People and Tribes
The majority ethnic group is the Shona (around 70%), followed by the Ndebele (about 20%). Smaller groups include Tonga, Venda, and several others. Traditional customs and languages play a vital role in rural communities.
Society
Zimbabwean society is rooted in communal traditions, respect for elders, and strong family bonds. Education is valued, and literacy rates are high despite economic challenges. Christianity is the dominant religion, blended in many cases with traditional beliefs.
Government
Zimbabwe is a presidential republic. The President is both head of state and government. It has a bicameral parliament consisting of the Senate and National Assembly. Political transitions have been controversial, with significant tension between the ruling party and opposition.
Economy
The economy is based on agriculture, mining, and services. Key exports include gold, tobacco, and platinum. Zimbabwe has faced hyperinflation, currency instability, and high unemployment, although reforms and international re-engagement efforts are underway.
Energy
Zimbabwe relies heavily on hydropower (notably the Kariba Dam), thermal power, and increasing solar investments. Power shortages are common, particularly during drought years.
Communications
Mobile phone penetration is high, and internet access is expanding, though rural connectivity remains limited. Providers include Econet Wireless, NetOne, and Telecel Zimbabwe.
Transportation
The country has an extensive but aging road and rail network. Major cities are connected by tarred roads, and the national airline, Air Zimbabwe, offers limited regional flights. Harare and Bulawayo are key transport hubs.
Transnational Issues
Zimbabwe has had land disputes with South Africa and internal land redistribution controversies. There have also been significant migration flows to neighboring countries due to economic hardship, particularly to South Africa and Botswana.
Fun Facts and Jokes
- Zimbabwe is home to the majestic Victoria Falls, one of the largest waterfalls in the world.
- Traditional Shona sculpture is internationally acclaimed and displayed in major global galleries.
- Joke: Why don’t Zimbabwean cows use WhatsApp? Because they already have good moo-nication!
- Joke: In Zimbabwe, we don't do inflation—our zeros just like to hang out!
Additional Information
Zimbabwe is a proud sporting nation with a strong cricket and football following. It also boasts rich biodiversity, with national parks like Hwange and Mana Pools drawing tourists and conservationists alike.
More Interesting Facts About Zimbabwe
- Zimbabwe is home to one of the world’s most famous natural wonders, the Victoria Falls, which is one of the largest and most powerful waterfalls in the world.
- The country is known for its rich wildlife, particularly in national parks such as Hwange National Park, which is home to one of the largest populations of elephants in Africa.
- Zimbabwe's currency, the Zimbabwean dollar, experienced one of the most extreme cases of hyperinflation in world history in the late 2000s, with prices rising at an astronomical rate.
- The Great Zimbabwe Ruins, located in southeastern Zimbabwe, are a UNESCO World Heritage site and are the largest ancient stone ruins in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Zimbabwe is famous for its craft industries, particularly the production of stone sculptures, which are highly regarded around the world for their quality and craftsmanship.
- The country boasts a number of world-class golf courses, and golf is a popular sport among Zimbabweans.
- Zimbabwe is a major producer of tobacco, with the industry contributing significantly to the country's economy through exports.
- Zimbabwe is home to the Matobo Hills, another UNESCO World Heritage site, which features rock art and ancient burial sites that date back thousands of years.
- The Zimbabwean national animal is the kudu, a type of antelope, which is a symbol of grace and beauty in the country.
- Zimbabwe is known for its strong and resilient music culture, with genres such as Chimurenga, sungura, and mbira music representing key cultural elements in the country's society.
Disclaimer: While every effort has been made to provide accurate and updated information, facts are subject to change. Please consult official Zimbabwean government sources or international agencies for the most current details.